You don’t notice it right away. A few extra minutes spent hunting through clinical documentation. A few denials trickling in each week. A claim here, a claim there, kicked back for correction. But over time, manual coding quietly drains your team’s time, energy, and accuracy.
It’s a slow and expensive burn.
For healthcare organizations juggling increasing volumes, evolving regulations, and shrinking margins, the need to do more with less is no longer optional. And this is where computer-assisted coding (CAC) steps into the spotlight.
So, what is CAC, exactly? What can it fix? Where does it fall short? And how do next-gen tools take things even further?
Let’s dive in.
The Challenge of Manual Medical Coding
Medical coding has always required both precision and speed. But today, coders are navigating even tougher challenges, such as:
- Ever-evolving guidelines like ICD-11, CPT, and HCPCS
- High volumes of patient encounters and the growing complexity of documentation
- Tight turnaround times, mounting compliance checks, and fewer coding resources
The stakes are high. Human errors can lead to claim denials, underpayments, or worse, noncompliance and audit risk.
And let’s not forget the very real impact on revenue cycle management (RCM). Delays in coding can slow down billing and choke cash flow. According to the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association (JAMIA), medical coding errors cost the US healthcare industry $36 billion annually in lost revenue, denied claims, and potential penalties.
In other words, medical coding is no longer a backend process; it is right at the core of your business functions.
What is Computer-Assisted Coding (CAC)?
Computer-assisted coding is exactly what it sounds like—it’s designed to assist human coders.
It leverages technology to scan clinical documentation, identify key medical concepts, and suggest the most appropriate diagnosis and procedure codes. Coders then validate, edit, or approve those suggestions.
However, that simple definition masks a great deal of sophistication. Modern CAC platforms bring powerful tech to the table.
How Does CAC Work?
Think of computer-assisted coding (CAC) as a digital co-pilot for medical coders. It doesn’t replace the coders and their expertise but quietly works in the background to speed things up.
Here’s how it works: CAC software scans through clinical notes and uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand what’s being said, even when the language is unstructured or nuanced.
Once it identifies key diagnoses, procedures, or symptoms, the system suggests matching codes. Behind the scenes, it relies on machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) to refine those suggestions over time. The more it’s used, the smarter it gets.
Most CAC systems are integrated with EHR or EMR platforms, allowing them to pull in real-time clinical data and return code suggestions directly within the coder’s workflow.
What Codes Can CAC Handle?
- ICD (International Classification of Diseases)
- CPT (Current Procedural Terminology)
- HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System)
The Benefits of Computer-Assisted Coding
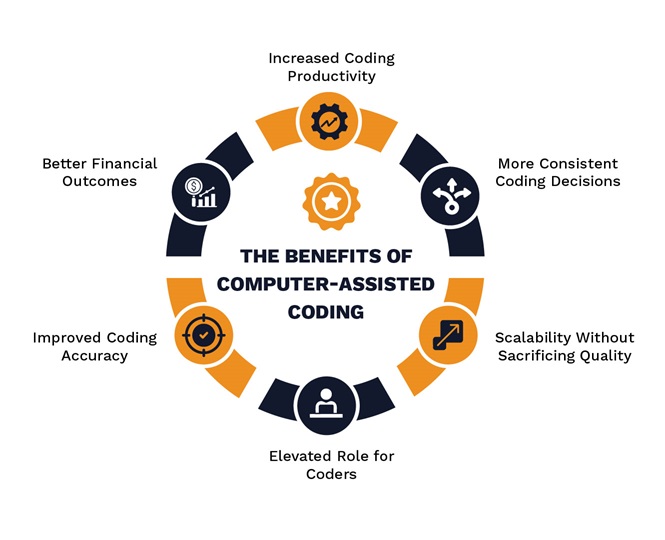
Based on real-world feedback from healthcare providers and coders, here are six ways computer-assisted coding is making a real impact:
Better Financial Outcomes
CAC doesn’t just make coding faster; it makes it smarter. Hospitals and health systems are seeing improvements in key revenue metrics. With cleaner codes and fewer denials, payments come faster and more accurately. Over time, the system helps identify documentation gaps and coder training needs, resulting in long-term financial improvements.
Increased Coding Productivity
With CAC taking care of the heavy lifting, coders don’t have to waste time hunting through documentation or re-entering the same data repeatedly. Many users report that the tool reduces the need for transcription and eliminates administrative burden. The result? Coders get more done, and organizations move through charts more efficiently.
Improved Coding Accuracy
CAC analyzes multiple parts of a patient’s record and ties them all together to generate accurate code suggestions. That means fewer missed codes, fewer costly mistakes, and better compliance. And because human coders still make the final call, there’s a built-in layer of quality control that strengthens the overall process.
Elevated Role for Coders
CAC doesn’t replace coders—it frees them. By removing repetitive and time-consuming tasks, the technology enables coding professionals to focus on higher-level work, such as improving clinical documentation, conducting compliance reviews, and performing internal audits. It’s not just a tech upgrade; it’s a career upgrade.
More Consistent Coding Decisions
We’ve all seen how coding can vary from person to person. CAC levels the field by applying coding guidelines consistently, day in and day out. That kind of consistency reduces payer disputes and gives healthcare leaders more confidence in their compliance data.
Scalability Without Sacrificing Quality
Whether your volume is growing or you’re preparing for seasonal spikes, CAC gives you the flexibility to handle it. Instead of stretching your team too thin, the software helps you maintain speed and accuracy under pressure. That kind of scalability is crucial for healthcare organizations seeking to expand without compromising quality.
The Challenges of Computer-Assisted Coding (CAC)
Although computer-assisted coding benefits include faster workflows and reduced errors, CAC comes with its own set of challenges that require careful navigation.
The Need for Human Oversight
What is CAC? It is an assistant, not a replacement for skilled coders. While computer-assisted coding excels at processing straightforward cases, complex or ambiguous scenarios involving rare conditions or incomplete notes often require human expertise to resolve. The CAC system may suggest codes, but it cannot interpret a nuanced clinical context. Therefore, without human oversight, inaccurate codes could result in billing errors or compromised patient care.
The solution? Treating CAC as a helping tool and always having human coders at your fingertips to come and save the day.Implementation Complexity
Setting up CAC in healthcare is a challenging task. The system needs to be tailored to an organization’s data and integrated with legacy tools, which can take weeks or even months of tweaking. Staff must learn new processes, and the transition can initially slow down operations. Costs add up, too—software, IT support, and hardware updates aren’t cheap.
The solution? Stay on top of change management in your organization, ensuring minimal disruption and maximum success. When it comes to cost, be sure to select the most suitable CAC tool for your organization, as it is a one-time investment.Data Quality Dependency
The strength of CAC coding rests on the quality of clinical records. If notes are vague or missing details, the system’s suggestions can be off the mark. For instance, a poorly documented diagnosis may lead to an incorrect billing code, resulting in potential complications & headaches down the line. Ensuring solid documentation requires clinician training and refined processes, which add effort to making the CAC work effectively.
The solution? Have a robust audit process in place to identify data inefficiencies before they are introduced into the system, thereby preventing issues.Constantly Chasing Updates
Medical coding rules change frequently, with new guidelines and regulations popping up regularly. A CAC system requires regular updates to remain compliant and accurate. If those updates lag, the system risks suggesting outdated codes, which can lead to rejected claims or compliance issues. Maintaining a current computer-assisted coding setup demands ongoing resources and attention, a challenge that can’t be ignored.
The solution? Integrate an AI autonomous medical coding software as it continually updates itself to reflect evolving coding standards and guidelines.
Introducing PCH Health: More than Just CAC
PCH Health’s autonomous coding platform is not your typical CAC tool. It combines the best of automation, AI, and workflow design to create a truly next-gen medical coding platform.
Here’s How PCH Health’s Coding Platform Goes Further:
- Autonomous Coding: Handles entire encounters without human intervention—perfect for high-volume, lower-complexity cases.
- AI Engine: Accurately assigns CPT, ICD-11, modifiers, and MIPS codes using deep learning and NLP.
- Productivity at Scale: Processes up to 12 encounters per second.
- Integrated User Platform: One dashboard. One system. All the data you need in one place.
- Expert Coding Support: A team of specialists ready to support edge cases or complex audits.
- Exclusive AAPC E/M Coding Calculator: Built-in intelligence from the industry's most trusted audit services team.
- Analytics Suite: Get real-time insight into coder productivity, QA checks, and claim statuses.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces coding costs by up to 25%.
Whether you’re coding for radiology, surgery, anesthesia, urgent care, or multispecialty groups, our autonomous coding platform scales to meet your needs.
Partnering For a More Efficient, Accurate Future
Computer-assisted coding has changed the game significantly. It not only addresses long-standing bottlenecks in medical coding but also helps improve compliance, speed, and consistency. But the industry isn’t stopping there!
With our autonomous medical coding platform, healthcare organizations can move beyond basic CAC and into a world of autonomous, intelligent, scalable medical coding.
So, the real question isn’t whether you need CAC. It’s what kind of CAC you’re choosing.
PCH Health’s autonomous medical coding solution is designed to address all modern-day coding challenges. Are you ready to take a peek at what we could do for your organization?
Contact us today for a walkthrough!
FAQs
Q1) What exactly is Computer-Assisted Coding (CAC)?
A) CAC is software that reads through medical records, like physician notes or lab reports, and suggests billing codes for diagnoses and procedures. It’s designed to speed up the coding process, helping healthcare teams work more efficiently while maintaining accuracy.
Q2) How does CAC improve accuracy in medical coding?
A) By analyzing clinical notes, CAC catches details that might slip past a coder, like matching a diagnosis to the correct code. It reduces typos and modifier errors, but coders still review the suggestions to ensure everything lines up with the patient’s care.
Q3) Does CAC replace human coders?
A) No, it doesn’t. CAC takes care of routine tasks, but complex cases—like unusual symptoms or unclear notes—need a human’s expertise. Coders are still essential for double-checking and making judgment calls, making CAC more of a partner than a replacement.
Q4) What does CAC stand for in healthcare?
A) CAC stands for Computer-Assisted Coding in healthcare.
Q5) What are the main benefits of CAC?
A) Better financial results, higher coder productivity, better coding accuracy, more consistent coding decisions, scalability without sacrificing coding quality, and more are some of the primary advantages of CAC.