A patient will go to the hospital, receive medication, let it work its magic, and head home. But once you step outside of that hospital, an incredibly complex system whirls into motion, which many still don't know about. This system is known as the insurance claims process, powering approvals and payments in healthcare.
Claim processing is vast, complicated, and extremely significant!
But what's fascinating is the claims adjudication process.
Claim processing involves a doctor or medical facility sending an invoice to a health insurance company once a patient starts receiving care. However, the hidden complexity lies in reimbursing those invoices.
Claims adjudication process helps settle or deny a claim received by an insurance company. The process allows payers to evaluate the medical claims and determine the amount to be reimbursed based on criteria such as coverage eligibility, medical necessity, billing and coding accuracy, and compliance.
A recent report by the Kaiser Family Foundation reported that the denial rate for healthcare claims is 18%, which highlights the heightened need for an effective and efficient claims adjudication process.
What is the adjudication process in healthcare claims processing?
A claim serves as a formal request for payment submitted by either a member or healthcare provider to a health insurer for services or items that could potentially fall under the insurer's coverage. These documents are essential for healthcare organizations seeking reimbursement from insurance companies. During the claims adjudication process, meticulous scrutiny is applied to ensure accuracy and relevance before determining whether the claim qualifies for coverage by the insurer.
The claims adjudication workflow typically moves through the following stages:
- The claim is initially accepted into the system and undergoes a basic information check. This check verifies that the claim is not a duplicate, ensures the accuracy of the patient's personal information, and confirms the absence of any omissions or errors.
- Subsequently, the claim proceeds to a more comprehensive verification process. This stage entails examining diagnosis and procedure codes and cross-referencing the patient's identification and date of birth with the insurer's records to validate their authenticity.
- Finally, a decision is generated on the claim. Depending on the outcome of the adjudication process, the claim is either approved and paid (either in full or partially), marked as pending for further review, or outright denied.
This structured workflow ensures thorough assessment and adherence to established criteria, thereby facilitating fair and efficient resolution of claims within the healthcare ecosystem.
The sections below discuss the steps involved in the claims adjudication process.
What are the steps of the claim adjudication process?
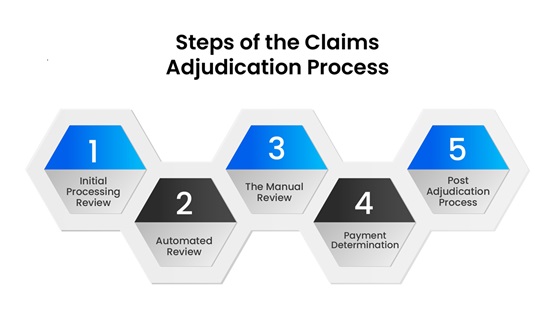
STEP 1: INITIAL PROCESSING REVIEW
The initial processing review is the first and most crucial step in the claim adjudication process. During this step, the payer checks claims for simple errors and omissions, where most claims end up getting denied.
Here, payers look for accurate information regarding:
- The patient's name
- The service code
- The date of service
- The diagnosis code
- The patient's subscriber identification number
- The patient's gender
If they fail during the accuracy check, the claims are returned to the healthcare organization that submitted them with the denied status.
According to an Equifax report, hospital bills exceeding $10,000 were found with an average error of $1,300.
Reports also show that poor billing practices cost providers $125 billion annually.
However, you don't need to worry—denials are not the end of the world. You can always resubmit the claims, but rework and resubmission can cost the provider valuable resources.
STEP 2: AUTOMATED REVIEW
If passed through the initial accuracy check, the claim moves into the automated review. Insurers use automated systems or algorithms to thoroughly examine the claim. They meticulously assess whether the healthcare service necessitates prior authorization and whether it is medically appropriate and cost-effective for the patient's condition. This stage typically resolves the majority of claims efficiently.
However, several common issues may arise during this automated review. Firstly, the claim must include the prior authorization number if the healthcare service requires prior authorization. Furthermore, the diagnosis and procedure codes in the claim must match those submitted for pre-authorization.
Additionally, insurance companies usually impose a 90 to 120-day deadline for claim submissions. The automated review system will deny claims that surpass this deadline.
Here's how automated review typically works in the claim adjudication process:
- Check the patient's eligibility on the date of service.
- Ensures presence and validation of pre-authorization or pre-certification.
- Confirm if the claim submitted is a duplicate or not.
- Check if the filing deadline has been met.
- Confirm if the process or diagnosis code is valid.
STEP 3: THE MANUAL REVIEW
Manual review refers to the human examination and assessment of a claim by a claims examiner or reviewer. This step typically occurs after the initial automated processing of the claim and is necessary for certain types of claims or situations that require human judgment, intervention, or clarification. Here's how the manual review process typically works:
- The claim is checked against predefined rules and criteria to determine whether it meets basic payment requirements, such as completeness, accuracy, and eligibility.
- Reasons for manual review may include complex medical procedures, high-dollar amounts, coding discrepancies, potential fraud or abuse indicators, or claims that fall outside standard processing guidelines.
- The claims examiner carefully evaluates the claim, analyzing supporting documentation, medical records, coding information, and any other relevant details.
STEP 4: PAYMENT DETERMINATION
The final two steps in the standardized adjudication process occur after a claim successfully passes through the three review phases discussed above. The final two steps represent how healthcare organizations ultimately receive payment from payers.
At a high level, there are three primary types of payment determinations that a claim may undergo:
- Paid: In this scenario, the payer has concluded that the claim is reimbursable based on its assessment. The healthcare organization receives payment for the services or items rendered.
- Reduced: If the payer determines that the billed service level for the diagnosis is excessively high, it may opt to "downcode" the procedure code to a lower level. The claim examiner makes this adjustment, resulting in a reduced payment to the healthcare organization.
- Denied: The payer considers the claim submitted as ineligible for reimbursement. In this case, the healthcare organization does not receive payment for the services or items outlined in the claim.
These determinations reflect the culmination of the adjudication process and significantly influence the financial outcomes for both healthcare providers and payers.
STEP 5: POST ADJUDICATION PROCESS
Even if claims successfully navigate the adjudication process without rejection, insurance payers may still conduct secondary auditing of these claims. This additional step aims to verify compliance with state or federal regulations, coding combinations, editing, and other guidelines. Through secondary auditing, payers ensure that claims adhere to all relevant standards and requirements, mitigating the risk of non-compliance and potential penalties.
This proactive approach helps maintain integrity within the claims management process and ensures that all claims are processed precisely and in accordance with established regulations.
Common challenges with claim adjudication in healthcare and how to overcome them?

Going through claim adjudication in healthcare poses several challenges, but proactive strategies can mitigate these obstacles. Here are the common challenges and ways to overcome common hurdles in the process:
Changing regulation and compliance needs:
Sticking with legacy applications restricts healthcare payers' capacity to adapt promptly. Dynamic, customizable applications offer a solution to this constraint. Additionally, legacy systems may hinder real-time processing, particularly when multiple systems require interaction.
While achieving real-time response in such scenarios is challenging, it's not unattainable. Auto-adjudication rates have notably increased, but real-time processing remains a goal yet to be fully realized.
Variations in provider-specific billing data:
Ensuring that every healthcare provider consistently provides all necessary information for a specific treatment can be challenging. Despite regulations governing claim billing, variations in provider’s system rules complicate the task of filling in all required details.
Technology offers a potential solution to this issue. Automated systems help avoid errors in provider billing data.
Claims demanding medical necessity review or clinical review:
Claims requiring clinical review or medical necessity review often involve complex medical procedures or treatments that necessitate a closer examination by healthcare professionals to determine their appropriateness and medical necessity.
In such cases, claims undergo a thorough clinical review process to ensure that the services rendered align with established medical guidelines and standards of care. This ensures that patients receive the most appropriate and effective treatments while preventing unnecessary costs and potential risks.
With various clinical decision system (CDS) tools available, this gap can also be addressed, streamlining the review process and enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of medical necessity determinations.
Fraud and abuse detection:
Detecting and preventing fraud and abuse in claims can be challenging, requiring sophisticated analytics and algorithms. Implementing fraud detection software and predictive modeling tools can help identify suspicious patterns and anomalies in claims data. Additionally, fostering collaboration between payers and law enforcement agencies to investigate and prosecute fraudulent activities can serve as a deterrent.
Manual processes and paper-based systems:
Relying on manual processes and paper-based systems can slow down the adjudication process and increase the risk of errors.
Transitioning to digital systems and automation tools for claims processing can improve efficiency and accuracy. Implementing electronic health record (EHR) systems and integrating them with claims management systems can streamline data exchange and reduce reliance on paper-based documentation.
Variability in payer policies:
Different payers may have varying policies and requirements for claim adjudication, leading to confusion and inefficiencies. Developing clear communication channels between payers and providers to clarify policies and requirements can help reduce misunderstandings.
Additionally, leveraging technology solutions that enable real-time access to payer policies and guidelines can streamline the adjudication process.
Provider and payer communication:
Poor communication between healthcare providers and payers can result in delays and misunderstandings during adjudication. Establishing clear communication channels and standardized protocols for claims submission and resolution can improve collaboration and efficiency.
Leveraging technology solutions such as electronic data interchange (EDI) and secure messaging platforms can facilitate real-time communication between providers and payers.
Conclusion
Imagine you are a bustling healthcare payer facing the daunting task of processing multiple claims daily. Amidst changing regulations and mounting pressure to maintain accuracy, errors and delays become inevitable.
However, with PCH Health's innovative healthcare solutions, you can easily overcome these challenges. By implementing advanced technology and customized strategies, PCH Health helps streamline the claims adjudication process, ensuring swift reimbursements and compliance adherence.
As a result, efficiency soars, errors plummet, and patients receive the care they deserve.
PCH Health has had a transformative impact on healthcare claims management for 40+ years. Talk to our experts to learn more about how our services can benefit your claims processing operations.