Every healthcare organization wants the same thing: better patient outcomes, stronger financial performance, and fewer compliance headaches. But getting there, especially under value-based care models, isn’t just about delivering care. It’s about how well you understand and document that care.
That’s where the Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF) score comes in. It’s the number that decides how much funding you’ll get to manage patients with complex needs. If your RAF score is off, your entire strategy — clinical, financial, and operational — can suffer.
For Medicare Advantage plans, ACOs, and providers working in value-based arrangements, the RAF score plays a direct role in funding, care planning, and compliance.
In this blog, we’ll break down what the RAF score is, how it’s calculated, why it matters, and how AI-powered autonomous coding platforms can help you stay ahead.
What Is a RAF Score, and How Is It Calculated?
The risk adjustment factor score is a numerical value used to estimate a patient’s expected healthcare costs. It is calculated by CMS (Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services) using a combination of demographic and clinical data, specifically diagnoses captured through medical coding.
Components of a RAF Score
RAF scores are built from two main components:
- Demographic Factors: Age, gender, Medicaid status, disability, and institutional living status
- Clinical Factors: Diagnoses that map to Hierarchical Condition Categories (HCCs) based on ICD-10 codes
Each HCC carries a numerical weight. In cases where multiple conditions fall into the same category, only the most severe (and highest weighted) condition counts toward the score.
RAF Score = Demographic Risk + Sum of HCC Weights
These scores are recalculated annually. That means providers must re-document chronic conditions each year to maintain their impact on RAF scores. CMS also updates its risk models regularly, such as the latest V28, which impacts how diagnoses contribute to RAF scoring.
Why RAF Scores Matter So Much
Financial Impact on Health Plans
Health plans rely on accurate RAF scores to determine monthly capitation payments from CMS under the Medicare Advantage program. If risk scores are too low due to missed or incorrect coding, plans receive less funding than they need to cover patient care. Overstated scores, on the other hand, can trigger audits and potential repayment demands.
Implications for Providers and ACOs
For organizations in value-based contracts, accurate Medicare risk adjustment means fair benchmarks and potentially more favorable shared savings. A higher, appropriately documented RAF score can support increased funding for complex care and the management of chronic conditions.
Better Care and Resource Allocation
RAF scores help identify high-risk patients, enabling care teams to intervene, monitor, and manage these individuals proactively. This supports targeted care coordination, preventive measures, and more effective population health management.
Compliance and Audit Protection
From a compliance standpoint, organizations must be ready for CMS RADV audits. These reviews assess whether submitted diagnoses are backed by documentation. Inaccurate RAF coding, whether due to omission or overstatement, can result in financial penalties or worse.
Common Challenges in RAF Score Optimization
Value or Incomplete Documentation
One of the most common challenges is the presence of vague or incomplete documentation. Why? Because coders can’t assign accurate ICD-10 codes if providers don’t clearly capture conditions in the medical record. For example, noting "diabetes" without specifying the type or complications leads to missed HCC opportunities.
Frequent Changes in Coding Guidelines
The CMS-HCC model evolves annually. New versions (like V28) can alter which diagnoses map to HCCs, change hierarchical relationships, or introduce new weights. Keeping up with these nuances demands ongoing coder education and deep familiarity with RAF medical rules.
Fragmented Data
Important diagnosis information is often spread across EHRs, lab systems, and billing software. When these systems fail to communicate with each other, coders and providers may miss critical data. As a result, the RAF score that healthcare organizations submit is often incomplete, leading to missed reimbursement opportunities.
Limited Provider Education and Engagement
Many clinicians are unaware of the financial and clinical implications of their documentation. Their focus is patient care, not coding. Without the right training or incentives, documentation often lacks the specificity and completeness required for accurate RAF Medicare reporting.
Heightened Audit Risk
CMS is increasingly aggressive in conducting RADV audits. Unsupported or inflated codes can lead to substantial clawbacks. Organizations that don’t establish internal compliance protocols risk both financial and reputational damage.
Best Practices for Improving RAF Scores
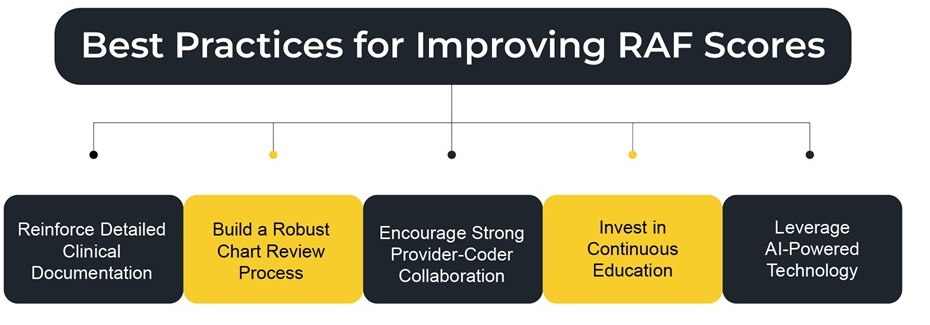
Reinforce Detailed Clinical Documentation
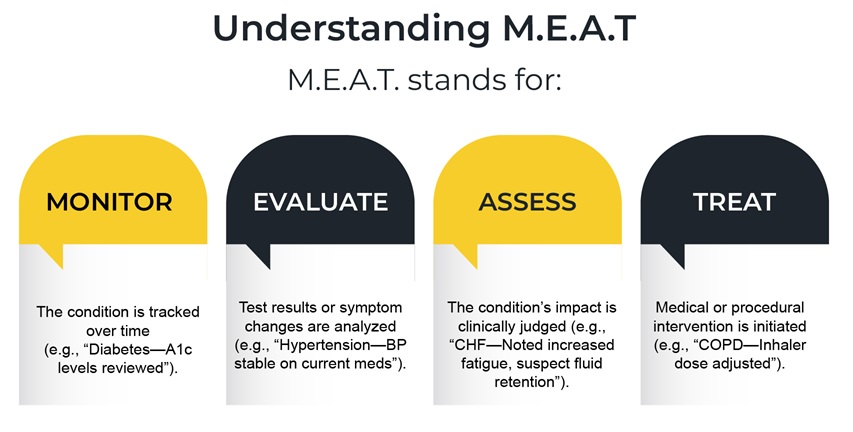
Ensure providers document all active conditions annually, clearly and completely. The condition must be explicitly noted and linked to a specific action, such as Monitoring, Evaluation, Assessment, or Treatment, as outlined in the M.E.A.T. framework. This level of coding is critical for defensible coding.
Build a Robust Chart Review Process
Prospective Reviews: Before claims are sent out, review the documentation and flag any missing diagnoses or incomplete narratives.
Retrospective Reviews: Audit charts post-submission to identify recurring issues, coding errors, or missed opportunities. Use findings to tailor training.Encourage Strong Provider-Coder Collaboration
Coders and clinicians should not operate in silos. Create structured feedback loops to flag, correct, and prevent documentation issues. Joint case reviews and coding rounds can improve mutual understanding and elevate documentation quality.
Invest in Continuous Education
Ongoing education is essential. Train coders and providers on the latest RAF score model changes, ICD-10 updates, and documentation requirements. Incorporate these training sessions into onboarding, CME modules, and regular review cycles.
Also, consider bringing in external auditors or consultants periodically to uncover blind spots and share industry benchmarks.Leverage AI-Powered Technology
Modern RAF medical tools, such as PCH Health’s autonomous coding platform, utilize natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to extract risk-adjusted data from clinical narratives. These platforms can:
- Automatically identify HCCs from free-text notes
- Suggest missed opportunities
- Flag unsupported diagnoses
- Ensure that every patient’s risk profile is complete and compliant
AI can also integrate data from multiple sources, unifying the patient record to create a holistic coding view.
Revolutionizing RAF Optimization with an AI Coding Platform
Even with strong documentation protocols, regular audits, and provider-coder collaboration, optimizing your risk adjustment factor score remains a complex and resource-intensive task. This is where PCH Health’s autonomous coding platform makes a measurable difference.
Our platform is designed to support the best practices you’ve put in place directly. It acts as an intelligent extension of your team, identifying coding opportunities, reducing gaps, and improving both accuracy and compliance in your RAF submissions.
Here’s how PCH Health enhances your RAF optimization efforts:
Our platform uses advanced natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) to extract clinically relevant information from provider notes. Unlike traditional systems that rely solely on structured fields, our platform understands the context through free-text narratives, meaning important diagnoses aren’t overlooked simply because they weren’t entered into a specific field.
- It matches ICD-11 codes to appropriate HCCs using CMS guidelines, improving the completeness of RAF scoring.
- It flags potentially undocumented or under documented conditions based on clinical indicators, giving coders a second layer of insight.
- The platform understands how complex conditions override lesser ones within the same HCC category, ensuring only the most appropriate codes are submitted.
- It keeps up with the CMS model changes without putting strain on your team to track every revision manually.
- Provides real-time coding support by making suggestions during or immediately after chart review, enabling coders to make informed decisions before submitting claims.
- Provides a transparent audit trail, allowing every code to be traced back to its documentation source.
Now that you know what PCH Health can do, imagine it in your workflows. Faster reviews, fewer gaps, and more confidence in every submission.
It starts with a simple step.
Book a quick demo to explore how it can be tailored to your practice’s requirements!
FAQ
Q1. What is a Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF) score, and why does it matter?
A) A Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF) score is used in healthcare to estimate the amount of care a patient may require based on their health conditions. It helps Medicare and other plans fairly reimburse providers who care for patients with more complex health needs.
Q2. How is a patient's RAF score calculated?
A) RAF scores are calculated using a combination of the patient’s age, gender, and documented medical conditions. RAF Score = Demographic Risk + Sum of HCC Weights
Q3. What are HCCs, and how do they tie into RAF scores?
A) HCCs (Hierarchical Condition Categories) are groups of health conditions that impact a patient’s RAF score. Each HCC adds weight to the score based on the seriousness of the condition. Accurate coding of HCCs helps reflect a patient’s true health risk.
Q4. Why is accurate RAF scoring important in value-based care?
A) In value-based care, payment is tied to patient outcomes. An accurate RAF score ensures providers are properly funded to manage patients with chronic or serious conditions.
Q5. How often should diagnoses be documented?
A) Diagnoses need to be documented annually. Even if a condition is ongoing, it must be recorded annually to ensure it’s captured in the patient’s RAF score and reflects their current health risk.
Q6. Why is clinical documentation important for RAF scores?
A) Clinical documentation is the foundation of RAF scoring. Complete and clear records help ensure that patients’ health risks are accurately captured, which supports the provision of appropriate care and payment.